The Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York has been running a lovely costume exhibit (“Death Becomes Her”, which closes tomorrow) covering mourning fashions roughly 1820-1920. I was invited to see it with a friend who knows how much I love costume history, and we recently spent seven hours at the museum, viewing many things in addition to the costume exhibit. We took a lot of photos –some will turn up in future blogposts! It was exciting to see two real examples of mourning gowns, from 1820 and 1824, that were worn at the end of our period. Don’t you love museums?
 The Regency era technically ended on January 29, 1820, when the old mad King George III died and Prinny succeeded to the throne. One reason his Coronation wasn’t held until the following year had to do with mourning customs –it wasn’t seemly for the royal family or the bereaved country to hold a grand celebration too soon after the death of the old monarch.
The Regency era technically ended on January 29, 1820, when the old mad King George III died and Prinny succeeded to the throne. One reason his Coronation wasn’t held until the following year had to do with mourning customs –it wasn’t seemly for the royal family or the bereaved country to hold a grand celebration too soon after the death of the old monarch.
Mourning customs followed by the upper classes at the personal level were even more de rigueur when it came to royal mourning, and the British had seen quite a lot of that by 1820. In November, 1817, Prinny’s only child, Princess Charlotte, died after giving birth to a stillborn baby. The old king’s Queen Consort, Charlotte, died in 1818. Prinny’s brother, the Duke of Kent, died just six days before their father, on January 23, 1820, so there was double mourning then. (The duke had won the race to produce the new heir to the throne with the birth of his daughter, Victoria, only eight months earlier.)
 It’s not known if this 1820 dress exhibited at the Met was worn for the decreed royal mourning or for a personal loss, or both, but its sheer overlay on the bodice and sheer sleeves were very fashionable. Compare the 1818 illustration below.
It’s not known if this 1820 dress exhibited at the Met was worn for the decreed royal mourning or for a personal loss, or both, but its sheer overlay on the bodice and sheer sleeves were very fashionable. Compare the 1818 illustration below.
My friend and I also loved this 1824 Scottish gown (below) embellished with ribbon trim and large scroll appliqués around the hem. But you can see clearly how the fashionable lady’s silhouette was changing from the slim columnar shape favored in the earlier years of the Regency!
 Wearing black for mourning dates as far back as the ancient Romans. As social mourning customs evolved, they dictated all levels of behavior –not only what you could and couldn’t do, but also what you were expected to wear, right down to the types of fabrics, for several distinct stages of mourning.
Wearing black for mourning dates as far back as the ancient Romans. As social mourning customs evolved, they dictated all levels of behavior –not only what you could and couldn’t do, but also what you were expected to wear, right down to the types of fabrics, for several distinct stages of mourning.
Widows were expected to mourn for at least two years, one of full mourning and one of the lighter half-mourning. Socializing was proscribed for at least six months to a year. Widowed men were not subject to the same expectations! The rules were less severe for the losses of other family members: a year to mourn parents and children, six months for siblings and grandparents, three months for aunts and uncles, and six weeks for cousins. Servants, and anyone in uniform, such as the military, wore black armbands. Door knockers were swathed in black to serve notice when a household was in mourning.

1818 Mourning Eveningwear
Naturally, the Regency fashionable were guided in all this by such venerable tomes as Ackermann’s Repository. (Research tip: you can find issues online by searching www.archive.org.) The February issue for 1820 features a number of examples of mourning dress, for after all, one needed to carry the mourning through all occasions in the course of a day. How do you like this walking dress, or these two versions of evening gowns?



The rules for public mourning were announced by the Lord Chamberlain’s office, and could vary. Prinny, now the uncrowned George IV, “in consideration of the interests of trade” declared a “shortened” period of public mourning for his father, essentially three months. The first stage lasted until March 19, just over six weeks of wearing bombazine and crape. The so-called “first change” or second mourning called for “plain black silk” with “French grey bombasine” for undress, until April, and then colored ribbons and flowers could be added to the black silk, or white with black trimmings could also then be allowed. Ackermann’s noted that in addition to French gray bombazine, pelisses made of gray levantine (trimmed with black velvet), and some “high dresses of poplin” (trimmed with black gauze or net) as well as gros de Naples and corded silk had been seen. Mourning was to end on April 30.
The exhibit at the Met offered a lot of fascinating details about the fabrics used for mourning clothes. For instance, crape was favored, they said, because while it satisfied the first stage requirement of having no sheen, its fine weave and flexibility made it very suitable to be pleated or crimped or shaped into purely decorative ornaments that allowed the wearer to be fashionable while still following the rules of mourning.
 While styles changed radically over the course of the 19th century, I noticed the same fabrics continued in use throughout. I have to include this picture of two dresses from the 1840’s, just for Susanna. Note the model’s “spaniel curls”!
While styles changed radically over the course of the 19th century, I noticed the same fabrics continued in use throughout. I have to include this picture of two dresses from the 1840’s, just for Susanna. Note the model’s “spaniel curls”!
I also have to include this photo (below) of two gorgeous sequin-covered 1902 evening gowns worn by Queen Alexandra (Victoria’s daughter-in-law) in half-mourning colors after Victoria’s death –they are mauve and purple–for Elena, because they are 100% sparkly!!
 However, advances of the Industrial Revolution: fabrics more available and less expensive, improved black dyes, and the boom in ready-made clothes after the invention of the sewing machine, served to support and spread the observance of mourning customs to the middle classes and beyond (more than Queen Victoria’s long mourning for Prince Albert). The “mourning trade” became big business after the Regency, with entire warehouses catering to the need for mourning attire. No doubt they had a vested interest in encouraging the fashion for public display, but if you went too far, you could be criticized for being ostentatious or, worse, insincere in your grief!
However, advances of the Industrial Revolution: fabrics more available and less expensive, improved black dyes, and the boom in ready-made clothes after the invention of the sewing machine, served to support and spread the observance of mourning customs to the middle classes and beyond (more than Queen Victoria’s long mourning for Prince Albert). The “mourning trade” became big business after the Regency, with entire warehouses catering to the need for mourning attire. No doubt they had a vested interest in encouraging the fashion for public display, but if you went too far, you could be criticized for being ostentatious or, worse, insincere in your grief!
 My heroine in The Persistent Earl is a widow. While I didn’t know as much about mourning customs and dress when I wrote that book as I do now, I tried to keep Daphne dressed appropriately in half-mourning colors. You may imagine my shock when I first saw the cover Signet gave that 1995 book –the heroine is depicted in a lovely, bright gold satin gown! When readers have asked me what scene in the story it represents, I’ve cheerfully told them it’s from AFTER the story ends. 🙂
My heroine in The Persistent Earl is a widow. While I didn’t know as much about mourning customs and dress when I wrote that book as I do now, I tried to keep Daphne dressed appropriately in half-mourning colors. You may imagine my shock when I first saw the cover Signet gave that 1995 book –the heroine is depicted in a lovely, bright gold satin gown! When readers have asked me what scene in the story it represents, I’ve cheerfully told them it’s from AFTER the story ends. 🙂
Today, the complex social rules of mourning that held sway during the Regency and flourished during the 19th century are mostly obsolete. People follow the customs dictated by their religions, but mourning is generally a private affair. Governments may order flags at half-staff for the death of important public figures, but there are no society-wide expectations or judgment laid down. Attitudes about mourning have changed. Do you think that is for the best? Are we better off sucking it up and trying to function as normally as we can manage instead of wallowing in our sorrows and making a public show of our grief? Or was there a kernel of common sense that we’ve lost underlying these old rules, that gave the grieving some recognition and respect, a bit of protection, structure, and time to recover? Please comment, for I’d really like to know what you think!
“She’d worn that color, or gray in its place, for three years now. And unrelenting black for a year before that. It had been a bit of a badge, she realized, a uniform of sorts. One never had to worry about who one was when one’s clothing proclaimed it so loudly.”
― Julia Quinn, When He Was Wicked
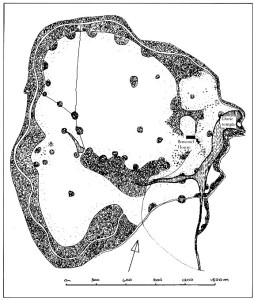
 Here’s his plan for Bowood House, with the Grecian temple on the right (east) point and how it looks today:
Here’s his plan for Bowood House, with the Grecian temple on the right (east) point and how it looks today: And talking of Capability Brown (his nickname came about from assuring his clients that their estates held great capabilities), let us not forget Terry Pratchett’s fictional Bergholt Stuttley “Bloody Stupid” Johnson from Discworld:
And talking of Capability Brown (his nickname came about from assuring his clients that their estates held great capabilities), let us not forget Terry Pratchett’s fictional Bergholt Stuttley “Bloody Stupid” Johnson from Discworld: